
What Is A Valheim Devoted Server & Tips On How To Make One
In addition, he enjoys cooking and enjoying guitar, is an avid horror and sci-fi reader, and is a fan of black steel music. Download the

No hay productos en el carrito.
No hay productos en el carrito.

No hay productos en el carrito.
No hay productos en el carrito.
Content

On the other hand, current assets in this formula are resources the company will use up or liquefy within one year. This current ratio is classed with several other financial metrics known as liquidity ratios. These ratios all assess the operations of a company in terms of how financially solid the company is in relation to its outstanding debt. Knowing the current ratio is vital in decision-making for investors, creditors, and suppliers of a company. The current ratio is an important tool in assessing the viability of their business interest.
On the other hand, the quick ratio will show much lower results for companies that rely heavily on inventory since that isn’t included in the calculation. Below is a video explanation of how to calculate the current ratio and why it matters when performing an analysis of financial statements. Of course, a higher current ratio is clearly more favorable to you, because this means that your company is able to handle its debts without any problems. On the other side, a low current ratio means that the company will have to sell off fixed assets in order to pay off its debts. The current ratio measures how well a company is able to meet its short-term obligations such as fixed operational costs and short-term debt.
One way to check for poor or greedy board members and executives is to look for signs of good will toward the long-term owner or shareholder. The more cash the executives send out the door and put in your pocket , the less money they have sitting around to tempt them to do something less than prudent. As an investor, you should note that a current ratio may be “good” in one field and only “fair” in another, and vice versa. The range and gauge of ratios will vary by industry due to the way each is funded, the rate at which cash cycles through, and other factors.
Expressed as a Number
For example, if a company's total current assets are $90,000 and its current liabilities are $72,000, its current ratio is $90,000/$72,000 = 1.25. If the current ratio of a business is 1 or more, it means it has more current assets than current liabilities (i.e., positive working capital).
It’s therefore important to consider other financial ratios in your analysis. In comparison to the current ratio, the quick ratio is considered a more strict variation due to filtering out current assets that https://kelleysbookkeeping.com/ are not actually liquid — i.e. cannot be sold for cash immediately. The formula includes all of a company’s current assets and excludes those that are difficult to convert into cash, such as inventory.
Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s free online accounting classes. Total-debt-to-total-assets is a leverage ratio that shows the total Current Ratio Formula amount of debt a company has relative to its assets. The current ratio is most useful when measured over time, compared against a competitor, or compared against a benchmark.
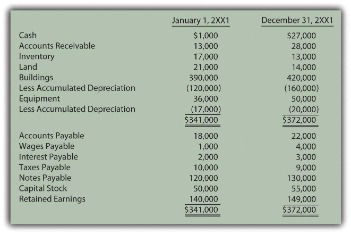
With different liquidity ratios, anyone can gain an accurate understanding of a company’s financial health and overall situation within minutes—read on to find out everything about these powerful formulas. The ratio that is used to derive a relation between the current assets and current liabilities of a firm is called a Current Ratio. It is used to determine whether the current assets of a firm would be sufficient to pay off its current obligations or not. In other words, it is used to depict the magnitude of current assets against current liabilities of a concern. Looking at any metric by itself or at a single point in time isn’t a useful way to measure a company’s financial health. Instead, it’s important to consider other financial ratios in your analysis and look at those ratios over an extended period.
Taking from the calculation above, MSFT has a current ratio of 2.53 which tells us they can cover their current obligations which is good. That said, to find a “good” current ratio you would need to know the average current ratio for the industry a company operates in. Based on what the average current ratio is for a specific industry you would be able to effectively gauge if the current ratio for a company is “good”. What’s important to clarify is the “high level” statement about the current ratio. The reason the current ratio is high level is for a few reasons one of which is that of inventory. In an event where they couldn’t move inventory as quickly, the company may not have enough liquid cash to pay current obligations.
In addition, he enjoys cooking and enjoying guitar, is an avid horror and sci-fi reader, and is a fan of black steel music. Download the
The clinician impact and financial cost to the NHS of litigation over pregabalin: a cohort study in English primary care PMC Please note that a
Trenbolone is a synthetic anabolic steroid that is commonly used by athletes and bodybuilders to enhance their muscle growth and performance. It belongs to Trenbolone